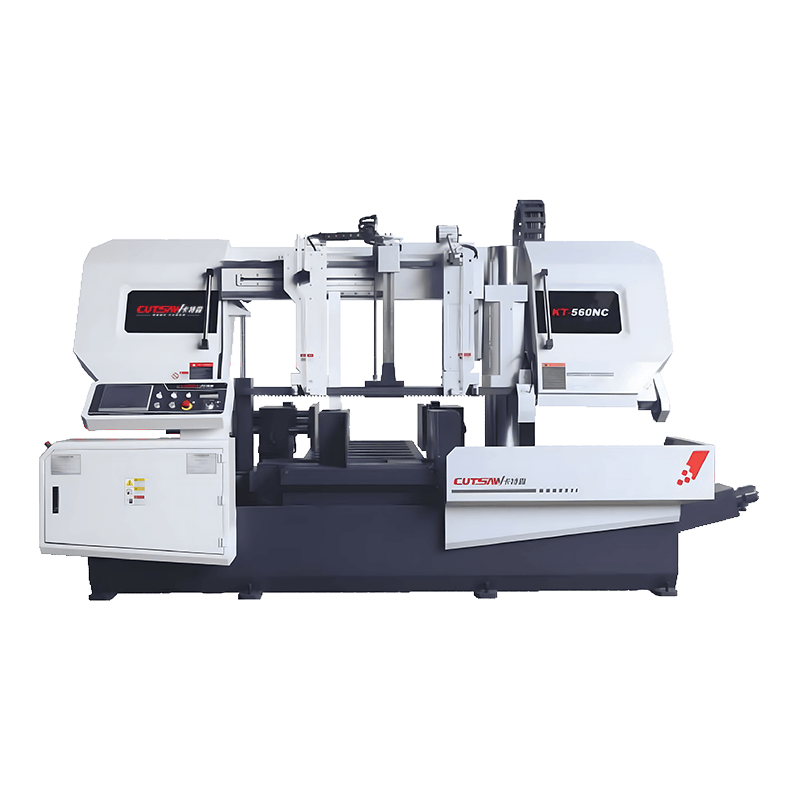
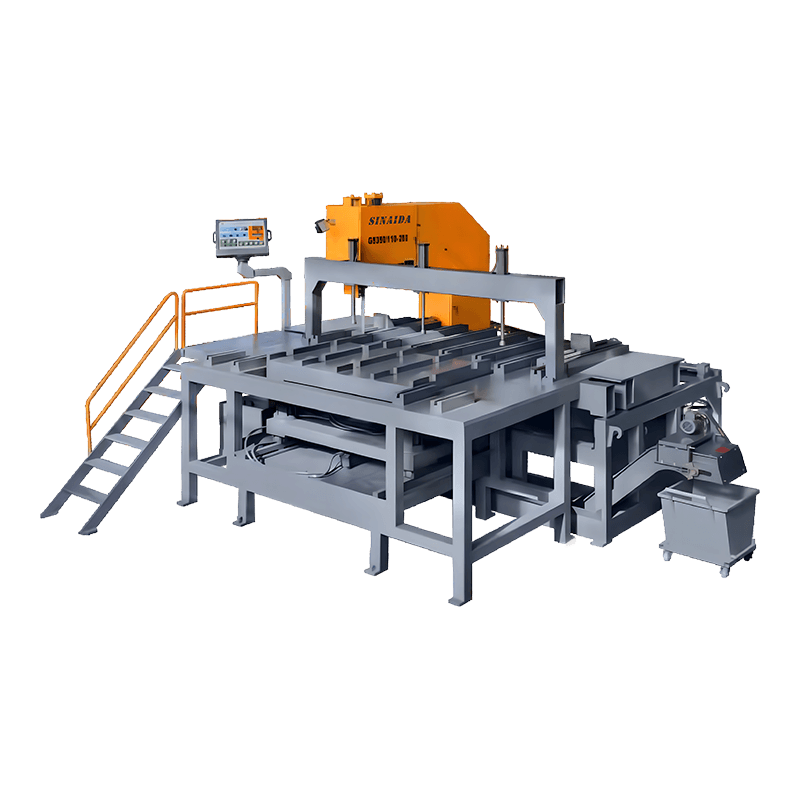
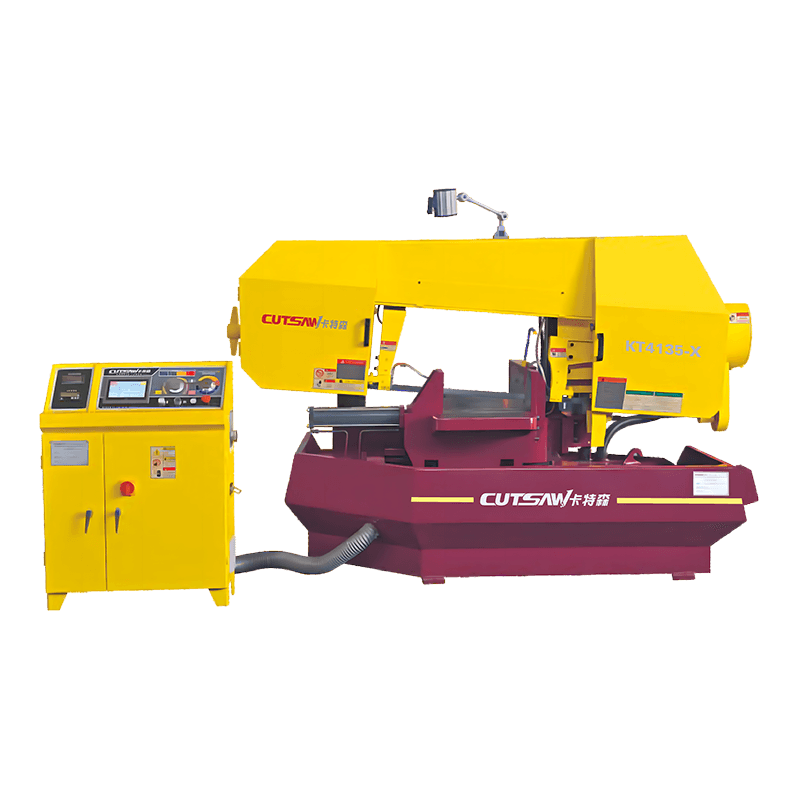
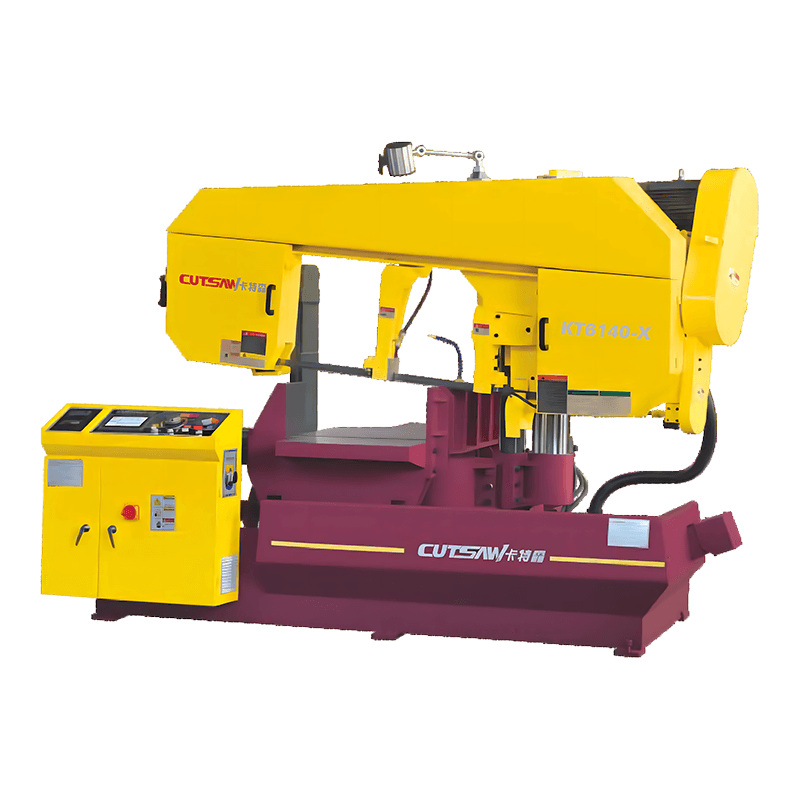
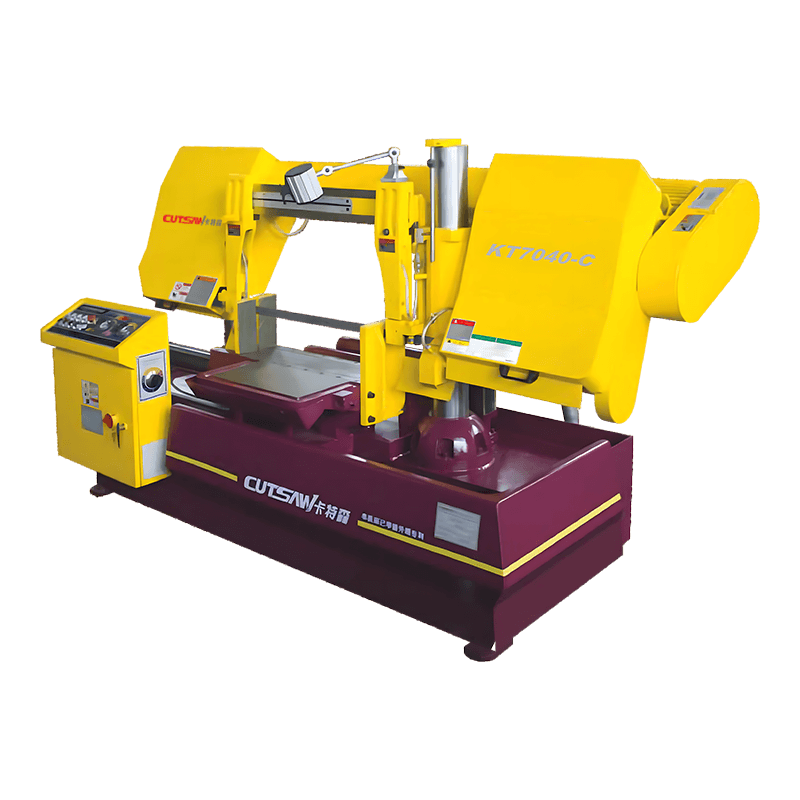
Rigid Frame Construction
The structural design of Angle Band Sawing Machine is a fundamental factor in controlling vibration and maintaining cut precision. High-quality machines are built with heavy-duty, rigid frames made from cast iron or reinforced steel, which absorb and dissipate the forces generated during cutting. The mass and stiffness of the frame reduce deflection of the saw head, blade, and workpiece, ensuring that the cutting path remains straight and consistent, even under heavy-duty applications. By minimizing frame oscillations, the machine not only produces more accurate and repeatable cuts but also transmits less vibration to the operator, reducing fatigue and improving overall workplace safety. Additionally, the rigid frame supports long-term durability, preventing misalignment or structural fatigue over extended use, which is critical for industrial and high-precision applications.
Precision Blade Guides and Tensioning Systems
Blade stability is crucial for controlling vibration in an Angle Band Sawing Machine. The machine employs precision blade guides, often mounted near both the entry and exit points of the cut, which prevent lateral blade movement and reduce deflection during operation. These guides maintain proper blade alignment under load, ensuring smooth, straight cuts without chatter or deviation. Complementing the guides, automatic or adjustable blade tensioning systems maintain consistent tension throughout operation. Proper tension minimizes blade flexing and skipping, reducing vibration, improving surface finish, and extending blade lifespan. Together, the blade guides and tensioning systems enhance cutting accuracy, especially when performing angled, miter, or compound cuts on dense or irregular materials. These features also reduce operational noise, contributing to a safer and more comfortable working environment.
Anti-Vibration Mounts and Damping Components
Modern Angle Band Sawing Machines incorporate anti-vibration mounts, damping pads, and internal stabilizers to further isolate and absorb vibrations. These components are typically installed beneath the motor, base, or saw head assembly and are made from resilient elastomeric or rubberized materials. They reduce high-frequency oscillations generated during cutting, particularly when processing hard metals, alloys, or thick stock. Internal damping plates or stabilizers within the frame absorb residual energy, preventing it from propagating through the machine structure. The result is smoother operation, enhanced cut quality, and a significant reduction in vibration transmitted to the operator. Reduced vibration also protects sensitive components, prolonging the life of the machine while maintaining consistent cutting performance over time.
Hydraulic or Servo-Driven Feed Systems
Controlled feeding mechanisms are a critical element in vibration reduction. High-end Angle Band Sawing Machines often utilize hydraulic or servo-driven feed systems to regulate the rate at which material is presented to the blade. Unlike manual or unregulated feeds, these systems maintain a consistent pressure and feed speed, preventing sudden jerks or resistance spikes that can cause blade chatter or vibration. Smooth, controlled feeding ensures that the blade cuts evenly through the material, improving both dimensional accuracy and surface finish. Additionally, regulated feed systems reduce operator fatigue by eliminating the need for manual exertion, which is especially beneficial during prolonged cutting sessions or when handling heavy, dense workpieces.
Workpiece Clamping and Support Systems
Proper stabilization of the material being cut is essential for vibration control and operator safety. The Angle Band Sawing Machine is equipped with adjustable clamps, vices, and fixture systems that secure the workpiece firmly during cutting. Some machines also feature rotating or tilting tables with locking mechanisms, allowing precise angle adjustments while keeping the material stable. By preventing workpiece movement, these systems reduce vibrations caused by slippage or uneven cutting forces. They also help maintain alignment, minimize blade deflection, and prevent unwanted contact between the blade and the workpiece that could compromise cut quality. For operators, these features reduce the physical effort required to hold heavy or irregularly shaped materials, enhancing comfort and minimizing strain over long shifts.